Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA)
- The purpose of Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) is to identify and evaluate the potential impacts(beneficial and adverse)of development and projects on the environmental system. It is a useful aid for decision making based on an understanding of the environmental implications including social, cultural and aesthetic concerns which could be integrated with the analysis of the project costs and benefits. This exercise should be undertaken early enough in the planning stage of projects for a selection of environmentally compatible sites, process technologies, and such other environmental safeguards.
- While all industrial projects may have some environmental impacts all of them may not be significant enough to warrant elaborate assessment procedures. The need for such exercises will have to be decided after an initial evaluation of the possible implications of a particular project and its location. The projects which could be the candidates for detailed Environment Impact Assessment include the following:-
- Those which can significantly alter the landscape, land use pattern and lead to concentration of working and service population;
- Those which need upstream development activity like assured mineral and forest products supply or downstream industrial process development;
- Those involving the manufacture, handling and use of hazardous materials;
- Those which are sited near ecologically sensitive areas, urban centers, hill resorts, places of scientific and religious importance.
- Industrial Estates with constituent units of various types which could cumulatively cause significant environmental damage.
- The Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) should be prepared on the basis of the existing background pollution levels vis-a-vis contributions of pollutants from the proposed plant. The EIA should address some of the basic factors listed below:
- Meteorology and air quality
Ambient levels of pollutants such as Sulphur Dioxide, oxides of nitrogen, carbon monoxide, suspended particulate matters, should be determined at the center and at 3 other locations on a radius of 10 km with 120 degrees angle between stations. - An additional contribution of pollutants at the locations are required to be predicted after taking into account the emission rates of the pollutants from the stacks of the proposed plant, under different meteorological conditions prevailing in the area.
- Hydrology and water quality
- The site and its surroundings
- Occupational safety and health
- Details of the treatment and disposal of effluents(liquid, air and solid) and the methods of alternative uses
- Transportation of raw material and details of material handling
- Control equipment and measures proposed to be adopted
- Meteorology and air quality
- Preparation of Environmental Management Plan is required for formulation, implementation, and monitoring of environmental protection measures during and after commissioning of projects.
Ministry of Environment & Forests
Environmental Impact Assessment Division E-Mail: secy@envfor.delhi.nic.in
some key elements of EIA
Scoping- identifying key issue and concern in interested parties
screening- deciding whether EIA is required on information collected.
mitigation- reviewing proposed action to prevent or minimize the potential adverse projects.
PROCESS OF EIA
PROJECT SCREENING
⇓
SCOPING
⇓
DEVELOPMENT
⇓
DESCRIPTION OF THE ENVIRONMENTAL BASELINE
⇓
IDENTIFICATION OF KEY IMPACTS
⇓
EVALUATION AND ASSESSMENT OF SIGNIFICANCE
⇓
IDENTIFICATION OF MITIGATION MEASURES
⇓
EIA PRESENTATION
⇓
REVIEW OF THE EIA
⇓
DECISION MAKING
⇓
POST DECISION MONITORING
⇓
AUDITING
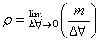

0 Comments