DEFINATION
When a liquid or solid dielectric placed in an external electric field , it's atoms becomes electric dipole which provides field which is different than applied field.the total field at the atomic sites is called the internal field or local field.it is represented by Ei or EL
E(local field)=E+p/3€
Determination of local field or internal field
In this article we derive the proper expression for the local field in the book for
the case of a uniform dielectric in a plane-plate capacitor. Consider the situation in
where we have a plane plate capacitor filled with a dielectric. We know
the average electric field in the dielectric, the field we have called E in the book.
E has two contributions
E = E0 + E1, (1)
where E0 = σ/.0 is the contribution from the charges on the plate of the capacitor
and E1 = −P/.0 is the contribution from the charges on the surface of the dielec-
tric. As discussed in the book, E1 opposes E0 und thus leads to a reduction of E.
In order to calculate the local field in the middle of the dielectric, we now “artifi-
cially” introduce two additional fields. Image a little sphere in the dielectric that is
small on the scale of the capacitor but large on an atomic scale. The sphere shall
be filled with dielectric as well, it is only an artificial construction to help with the
calculation because we can calculate the field from everywhere except the inside
of the sphere macroscopically and then the field from the inside of the sphere mi-
croscopically. We can write the total field at the point in the centre of the sphere
as
Eloc = E0 + E1 + E2 + E3 = E + E2 + E3, (2)
where E2 and E3 are the fields created by the charges on the surface of the sphere
and by the microscopic inside of the sphere, respectively.


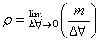

0 Comments