Semiconductor
solid substance that has a conductivity between that of an insulator and that of most metals(conductors), either due to the addition of an impurity or because of temperature effects. Devices made of semiconductors, notably silicon, are essential components of most electronic circuits.
Elemental semiconductors include antimony, arsenic, boron, carbon, germanium, selenium, silicon, sulfur, and tellurium. Silicon is the best-known of these, forming the basis of most integrated circuits (ICs). Common semiconductor compounds include gallium arsenide, indium antimonide, and the oxides of most metals. Of these, gallium arsenide is widely used in low-noise, high-gain, weak-signal amplifying devices.At room temperature resistivity of semiconductor is in between insulators and conductors. Semiconductors show a negative temperature coefficient of resistivity that means its resistance decreases with an increase in temperature. Both Si and Ge are elements of IV group i.e. both elements have 4 valence electrons. Both form the covalent bond with the neighboring atom. At absolute zero temperature both behave as insulator i.e. the valence band is full while the conduction band is empty but as the temperature is raised more and more covalent bonds break and electrons are set free and jump to the conduction band.

Intrinsic Semiconductors-
As per the theory of semiconductor, semiconductor in its pure form is called as an intrinsic semiconductor. In pure semiconductor number of electrons (n) is equal to the number of holes (p) and thus conductivity is very low as valence electrons are covalent bonded. In this case, we write (n = p)
Extrinsic Semiconductors-
As per the theory of semiconductors, impure semiconductors are called extrinsic semiconductors. An extrinsic semiconductor is formed by adding a small amount of impurity. Depending on the type of impurity added we have two types of semiconductors: N-type and P-type semiconductors. In 100 million parts of semiconductor one part of impurity is added.N-type Semiconductor
In this type of semiconductor, majority carriers are electrons and minority carriers are holes. An N-type semiconductor is formed by adding pentavalent (five valence electrons) impurity in a pure semiconductor crystal, e.g. P. As, Sb.
P-type Semiconductors-
in this type of semiconductor majority carriers are holes and minority carriers are electrons. A P-type semiconductor is formed by adding trivalent ( three valence electrons) impurity in a pure semiconductor crystal, e.g. B, Al Ba.
structure of silicon-
it contains 4 free electron which makes it different from other materials.
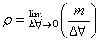

1 Comments