defination
The branch of chemistry that deals with the phenomena that occurs at the
surfaces or the interfaces is known as Surface Chemistry. A lot of properties of
matter such as solids and liquids depend on the nature of the surface. Let us
learn introduction about Surface Chemistry through chemistry lecture notes.
- The phenomenon of attracting and retaining the molecules of a substance at
molecules on the surface than in the bulk is known as adsorption. Adsorption
results in decrease of surface energy.
- Examples of Adsorption:
a) Adsorption of a gas by Charcoal: Finely grounded activated charcoal adsorb
a gases like ammonia, sulfur dioxide, chlorine, hydrogen, carbon monoxide,
phosgene. Charcoal is the adsorbent whereas the gas molecules acts ass adsorbate.
b) Adsorption of a dye by Charcoal: The dye gets adsorbed on the surface of
the animal charcoal when the animal charcoal is shaken with an organic dye
solution. For example, methylene blue. It turns colourless due to adsorption.
c) Air in presence of silica gel: Water molecules get adsorbed on the silica gel.
This make the air dry
- constituents of Adsorption Process:
The adsorption process consists of two types of substances:
- Adsorbent: The solid substance on the surface of which adsorption occurs
- Adsorbate: The substance which gets adsorbed on the solid surface due to
be a gas or a solute some solution.
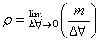

0 Comments