What is the atmosphere?
The atmosphere is the mixture of gases and water vapor which surrounds any planet system.
E.g. For earth, these gases are oxygen, carbon dioxide, nitrogen and water vapor, etc.
The atmosphere is classified into five parts-
- Troposphere
- Stratosphere
- Mesosphere
- Thermosphere
- Exosphere*
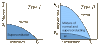
 |
| segments of atmosphere |
Earth's atmosphere is about 300 miles (480 kilometers) thick, but most of it is within 10 miles (16 km) the surface. Air pressure decreases with altitude. At sea level, air pressure is about 14.7 pounds per square inch (1 kilogram per square centimeter). At 10,000 feet (3 km), the air pressure is 10 pounds per square inch (0.7 kg per square cm). There is also less oxygen to breathe
The troposphere is the layer closest to Earth's surface. It is 4 to 12 miles (7 to 20 km) thick and contains half of Earth's atmosphere. Air is warmer near the ground and gets colder higher up. Nearly all of the water vapor and dust in the atmosphere are in this layer and that is why clouds are found here.
The stratosphere is the second layer. It starts above the troposphere and ends about 31 miles (50 km) above ground. Ozone is abundant here and it heats the atmosphere while also absorbing harmful radiation from the sun. The air here is very dry, and it is about a thousand times thinner here than it is at sea level. Because of that, this is where jet aircraft and weather balloons fly.
The mesosphere starts at 31 miles (50 km) and extends to 53 miles (85 km) high. The top of the mesosphere, called the mesopause, is the coldest part of Earth's atmosphere, with temperatures averaging about minus 130 degrees F (minus 90 C). This layer is hard to study. Jets and balloons don't go high enough, and satellites and space shuttles orbit too high. Scientists do know that meteors burn up in this layer.
The thermosphere extends from about 56 miles (90 km) to between 310 and 620 miles (500 and 1,000 km). Temperatures can get up to 2,700 degrees F (1,500 C) at this altitude. The thermosphere is considered part of Earth's atmosphere, but air density is so low that most of this layer is what is normally thought of as outer space. In fact, this is where the space shuttles flew and where the International Space Station orbits Earth.
gases in the atmosphere-
 |
| temperature contribution curve with gases contribution |

0 Comments