Introduction
The 1996 Nobel Prize for Chemistry has been won by Harold W. Kroto, Robert F. Curl and Richard E. Smalley for their discovery in 1985 of a new allotrope of carbon, in which the atoms are arranged in closed shells.
They are molecules composed entirely of carbon, in the form of a hollow sphere, ellipsoid, or tube.
Spherical fullerenes are sometimes called buckyballs, the C60 variant is often compared to a typical white and black soccer football.
DEFINATION
Fullerenes is a form of carbon having a large spheroidal molecule consisting of a hollow cage of sixty or more atoms, of which buckminsterfullerene was the first known example.Structure of fullerenes-
Fullerenes consist of 20 hexagonal and 12 pentagonal rings as the basis of an icosohedral symmetry closed cage structure Each carbon atom is bonded to three others and is sp2 hybridised. The C60 molecule has two bond lengths - the 6:6 ring bonds can be considered "double bonds" and are shorter than the 6:5 bonds.C60 is not "superaromatic" as it tends to avoid double bonds in the pentagonal rings, resulting in poor electron delocalisation. As a result, C60 behaves like an electron deficient alkene, and reacts readily with electron rich species. The geodesic and electronic bonding factors in the structure account for the stability of the molecule. In theory, an infinite number of fullerenes can exist, their structure based on pentagonal and hexagonal rings, constructed according to rules for making icosahedra.
Fullerenes, or buckminsterfullerenes in full, are molecules composed entirely of carbon, taking the form of a hollow sphere, ellipsoid, tube or ring.Fullerenes are similar in structure to graphite, which is composed of a sheet of linked hexagonal rings, but they contain pentagonal (or sometimes heptagonal) rings that prevent the sheet from being planar.
Properties of fullerenes
- Fullerenes consist of 20 hexagonal and 12 pentagonal rings as the basis of an icosohedral symmetry closed cage structure.
- Each carbon atom is bonded to three others and is sp2 hybridised.
- The C60 molecule has two bond lengths - the 6:6 ring bonds can be considered "double bonds" and are shorter than the 6:5 bonds.C60 is not "superaromatic" as it tends to avoid double bonds in the pentagonal rings, resulting in poor electron delocalisation.
- C60 behaves like an electron deficient alkene, and reacts readily with electron rich species.
application of fullerine-
- Photo detectors and photo voltaics
- Polymer Electronics
- Antioxidants & Biopharmaceuticals
- Polymer Additives
- Catalysts
- nanomaterials


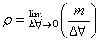

0 Comments